Neurofeedback
Neurfeedback is like having a mirror image of your brain fed back to you through tactile visual and audio feedback which allows your brain to recognize and correct inconsistent patterns.
Neurofeedback is a therapeutic technique that trains individuals to regulate their brainwave activity. It works by providing real-time feedback on brainwave patterns, allowing the individual to learn how to increase or decrease specific brainwave frequencies associated with improved focus, organization, and emotional regulation.
The benefits of neurofeedback can be long-lasting, as it helps to rewire the brain’s neural pathways (plasticity), leading to lasting improvements in attention and behavior regulation. Studies have shown that individuals who undergo neurofeedback training can experience significant reductions in symptoms of ADHD, Anxiety, depression, OCD, sleep disturbances, and mood disorders.
Many people maintain these improvements long after the training ends. Unlike temporary fixes like medication, which may need to be adjusted over time or may cause side effects, neurofeedback aims to create lasting changes in brain function that continue to support cognitive performance and emotional balance. While the process requires commitment and multiple sessions, the potential for lasting, permanent improvements in symptoms makes neurofeedback an increasingly popular and promising option for managing the disorder without reliance on medication.
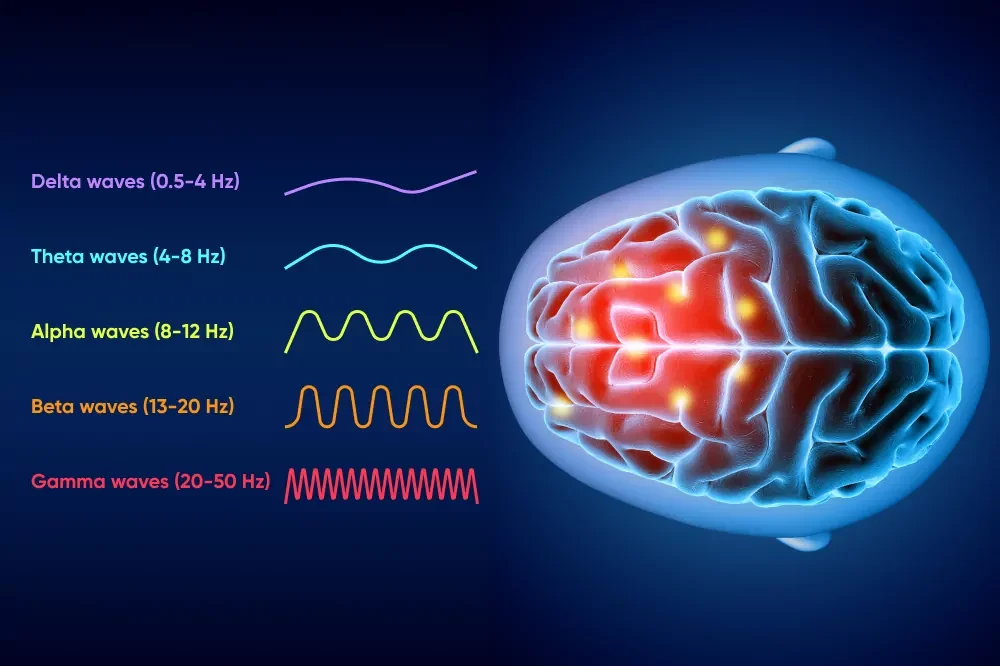
About Brainwaves
Delta waves (0.5-4 Hz): Slowest waves, often seen during deep sleep or relaxation
Theta waves (4-8 Hz): Associated with drowsiness, meditation, and creativity
Alpha waves (8-12 Hz): Typically seen during relaxed states, closed eyes, and decreased cortical activity
Beta waves (13-20 Hz): Faster waves, often associated with attention, problem-solving, and mental activity
Gamma waves (20-50 Hz): Fastest waves, linked to high-level cognitive processing and memory consolidation
